Introduction Rinderpest
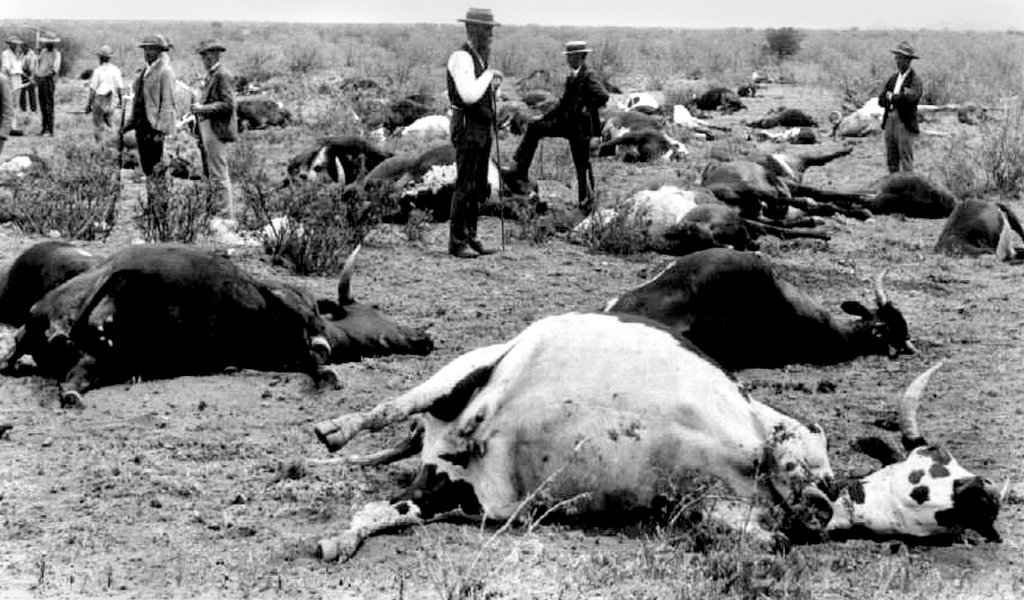
Rinderpest (also cattle plague or steppe murrain) was an infectious viral disease of cattle, domestic buffalo, and some other species of even-toed ungulates, including buffaloes, large antelope and deer, giraffes, wildebeests, and warthogs. It is characterized by the fever, oral lesion, persistent diarrhea, lymphoid leuckosis and high mortality rate. It is also called pest of bovine. Indica called as “MATTA”.

Rinderpest Etiology:
Causative agent of Rinderpest belongs to family Paramyxovaridae, genus ” Morbilli” virus. It is irradiated from PAKISTAN but some cases are present due to trade issues.
Why it is easy to eradicate?
- Rinderpest is easy to eradicate because virus has one serotype.
- Recovered or vaccinated animals remain immune throughout the life.
- no vertical transmission is reported
- no arthropod is involved (no vector)
- no carrier stage exist.
Epidemiology:
- Disease mainly effect bovines but rarely in pigs.
- Outbreak mostly observed in middle east , Asia and tropical Africa.
- It is highly contagious disease.
- Mortality rate up to 100%
- transmission occurs directly or indirectly.
Pathogenesis:
After inhalation or ingestion of virus , it goes to the sub-mandibular & pharyngeal lymph nodes, where it start to multiply, after multiplication the virus enters into blood and develop viremia within 3 days of infection from where the virus moves to mucosa of GIT and respiratory tract & lead to leukopenia that may lead to severe immunosuppresion. viruses shedding is continuous during acute phase and sub divide when body temperature returns to normal.
Clinical Findings:
- The incubation period of Rinderpest(Mobilli virus) is 3 to 9 days.
- disease occurs in four forms Per acute, Acute, sub acute and atypical form.
Per acute:
Atypical form:
- Open dead body observe necrotic erosions and hemorrhages in mouth Git and URT.
- Hemorrhages seen in transverse fashion colon that gives appearance of Zebra so it is ZEBRA STRIPPING.
- enlarged and adematous lymph nodes.
- Gall bladder is hemorrhagic and white foci observed in pair patches.
Diagnosis of Rinderpest:
- on the basis of history. Contagious viral disease increases in form if today 20 cases then tomorrow 30 cases occurs.
- vaccination and deworming done in healthy animals.
- on the basis of clinical signs Oral lesions persistent diarrhea.
- chronic nature of diarrhea & constipation lead to Rinderpest.
Treatment of Rinderpest:
- no known treatment of Rinderpest.
- notify to higher officers at time
- strict Quarantine measures should be adopted
- cell culture vaccine for rinderpest.